论文地址:MoEBERT:from BERT to Mixture-of-Experts via Importance-Guided Adaptation
MoEBERT:MoE+distillation
Abstract
目前训练小的压缩的模型是通过知识蒸馏,但性能下降厉害,因此提出用MoE-BERT来提升模型性能和推理速度。初始化MoE-BERT通过把FFN适应到多个专家里,同时还提出了layer-wise distillation方法来训练MoE-BERT
Introduction
蒸馏方法分为任务无关和任务特定两种
- task-agnostic:预训练student然后在下游任务微调
- task-specific:从预训练好的模型初始化然后微调
本工作主要关注任务特定的蒸馏
但是MoE模型从零开始训练很难而且参数量大,所以采用MoE架构在预训练模型中用于微调,提升推理速度的同时保持表征性能
比如BERT-base的FFN维度是3072,换成4个expert,每个768
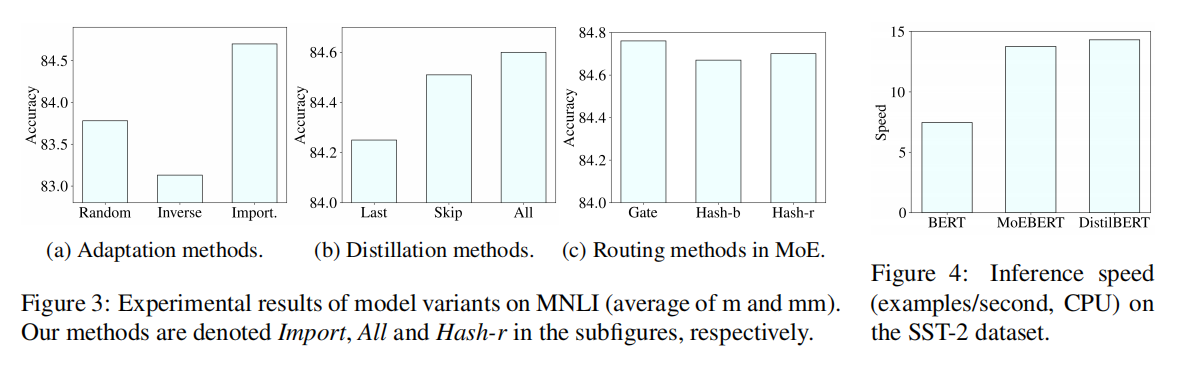
为了把FFN适配到experts里,提出了一种基于重要性的方法,根据经验,FFN里面有些神经元对模型性能的贡献比其他大,移除这些神经元会有巨大的性能损失,这种性质可以用importance score来定量。因此在experts中共享重要的神经元,其他的均匀分布
Background
Backbone: Transformer
FFN定义,两层全连接一个激活函数
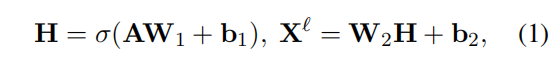
Mixture-of-Experts Models
$a_t$ 是attention output A的第t行,l是层数
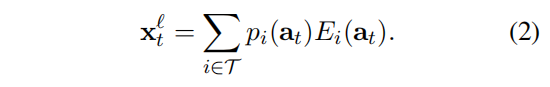
计算 $p_i$ 的方法很多,比如用全连接矩阵
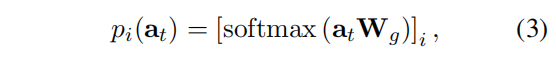
但是这个方法当所有输入都被路由到同一个expert的时候就坍塌了
为了解决这个问题有的方法启发式的,如加高斯噪声,限制到某专家的最大路由数,引入负载平衡损失,使用线性赋值等
与之对应的工作是完全删除了gate,使用哈希函数预先分配标记给专家,这样 $p_i=1/K$
一个token只激活K个专家,通常K<<N
Method
Importance-Guided Adaptation of Pre-trained Language Models
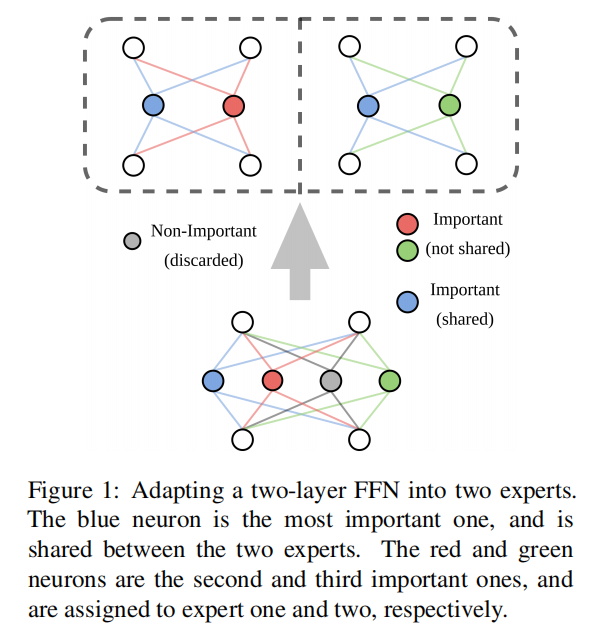
把FFN随机转移到experts里面效果很差,因此引入重要度分数(最开始是在模型剪枝里面用到的),对于一个数据集D,样本对 ${(x,y)}$ ,分数定义如下:
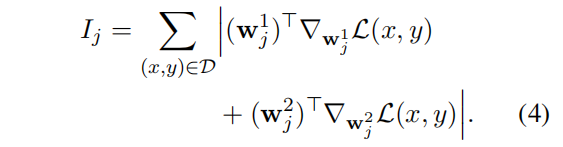
其中 $w_j^1\in \mathbb{R}^d$ 是 $W_1$ 的第j列, $w_j^2\in \mathbb{R}^d$ 是 $W_2$ 的第j行
公式4的重要度分数表示如果移除神经元的损失变化
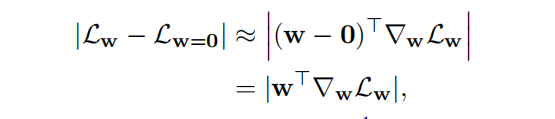
这里的近似是基于 $L_w$ 在w=0的一阶泰勒展开式
计算完了所有列的 $I_j$ 后排序,选出top-s,这样每个expert的列是 ${w_{(1)^1},···,w_{s}^1,w_{(s+e)}^1,w_{(s+e+N)}^1,···}$
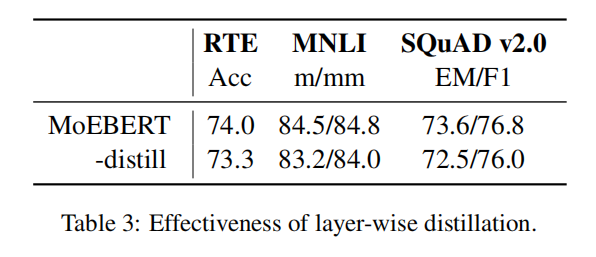
Layer-wise Distillation
transformer layer distillation loss:
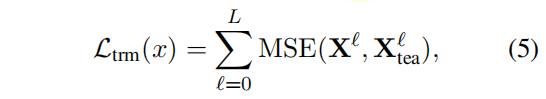
prediction layer distialltion loss:
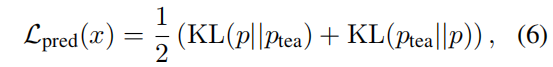
layer-wise distillation loss:
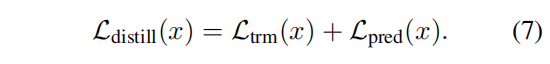
Model Training
使用随机哈希策略训练experts,每个token预先分配给一个随机的expert,在训练和推理的时候这个分配关系不改变,这种分配策略和其他的路由策略进行了比较
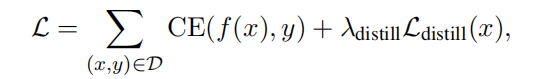
Experiments
Datasets
GULE、Question Answering
Implementation Details
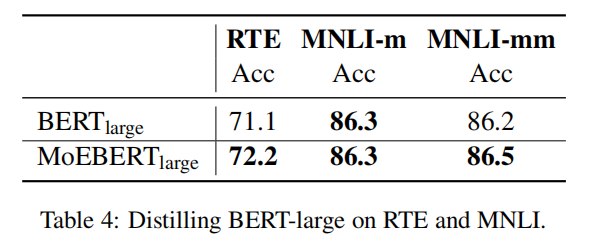
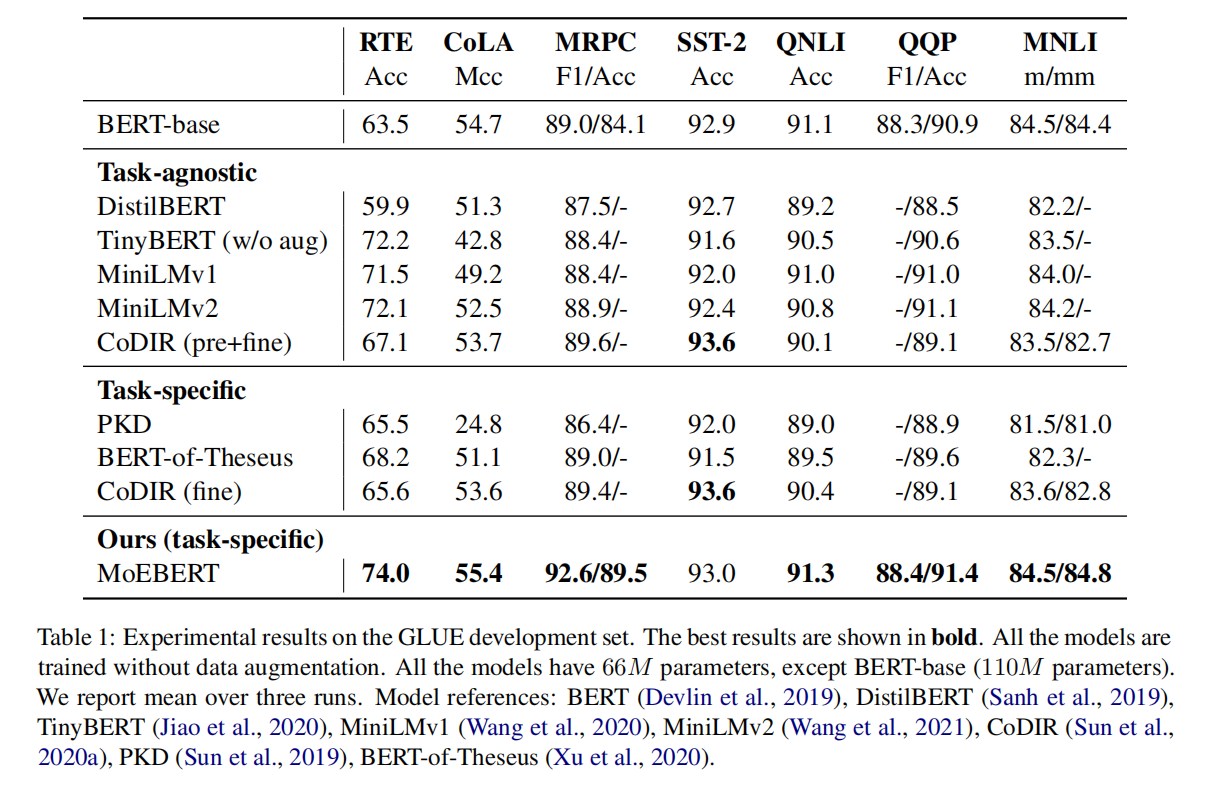
用BERT-base当student和teacher,先把预训练好的迁移到MoE模型,然后再做layer-wise task specific知识蒸馏。专家数量是4,维度768,选的是top-512
Main Results
Ablation Study
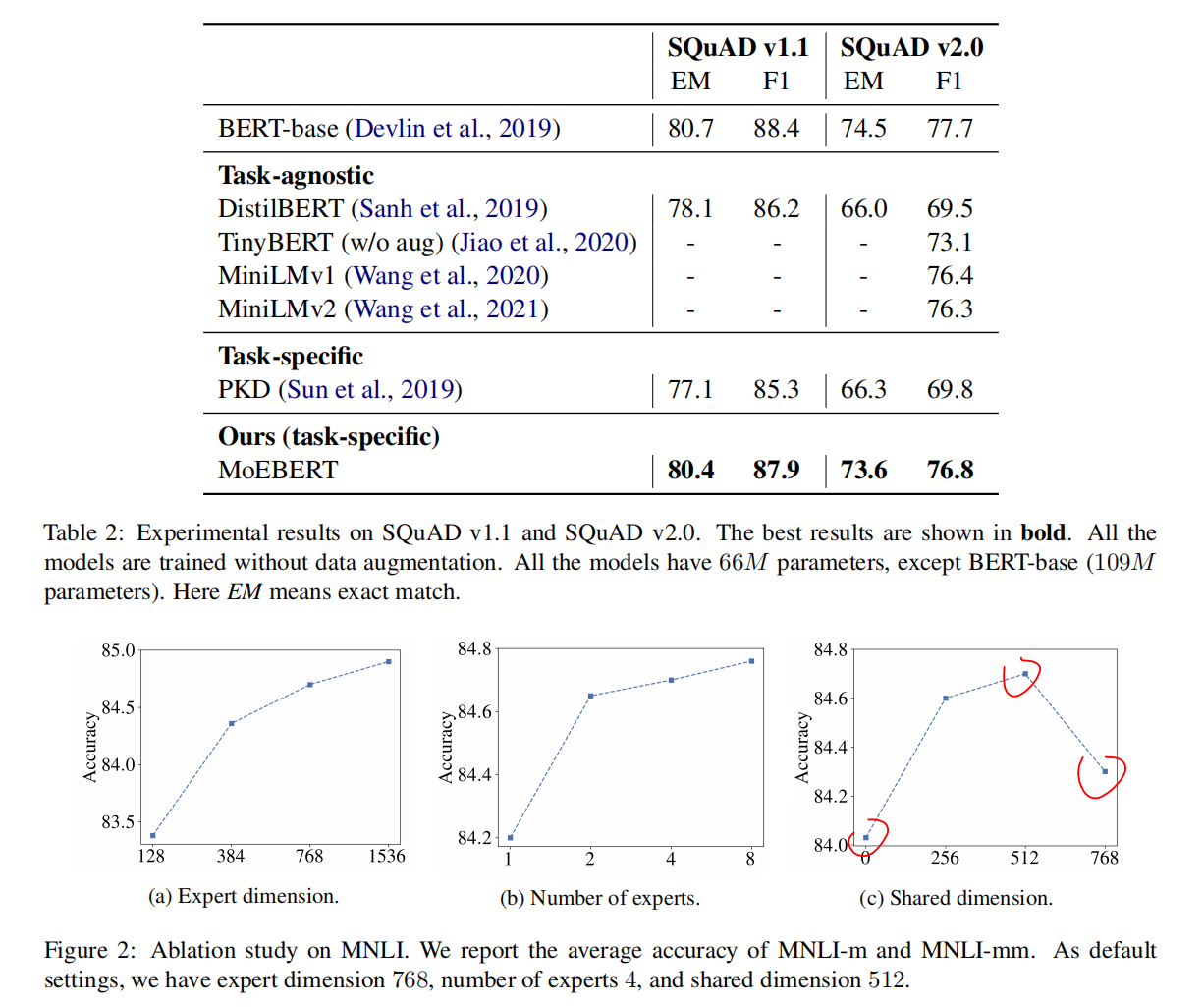
共享的维度太多了可能也有问题,缺乏专家的多样性
Analysis